Was this page helpful?
Caution
You're viewing documentation for a previous version. Switch to the latest stable version.
ScyllaDB Read Repair¶
Read repair serves as an anti-entropy mechanism during read path.
On read operations, Scylla runs a process called read repair, to ensure that replicas are updated with most recently updated data. Such repairs during read path run automatically, asynchronously, and in the background.
Note however, that if digest mismatch is detected before consistency level is reached, that repair will run in the foreground.
A normal read operation works according to the scenarios described in our Fault Tolerance documentation.
Read Request¶
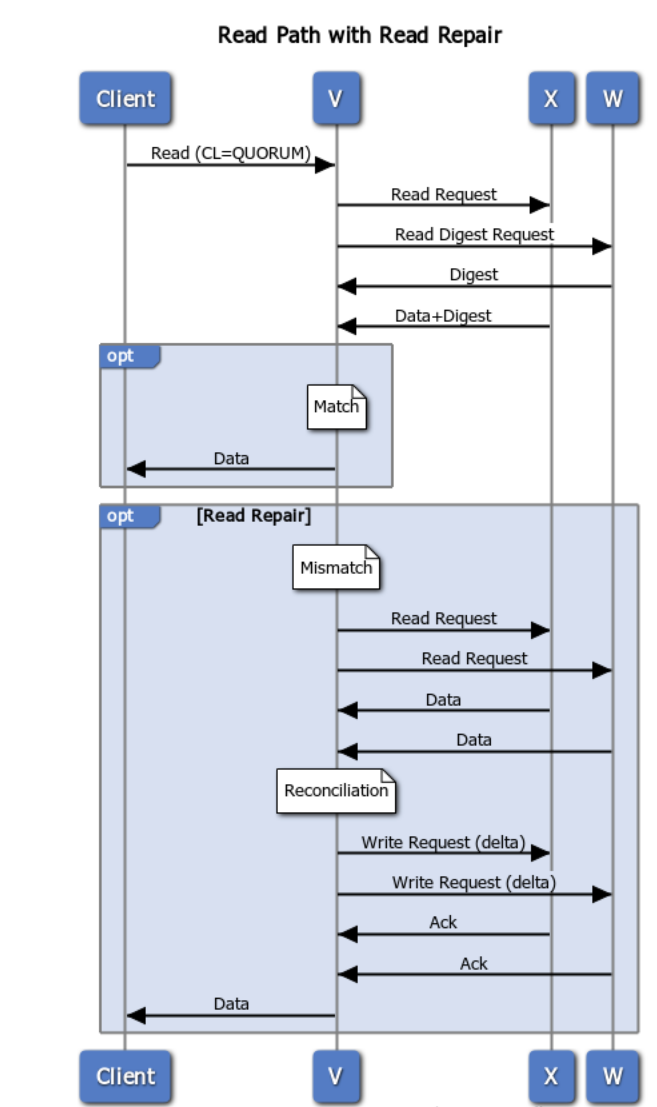
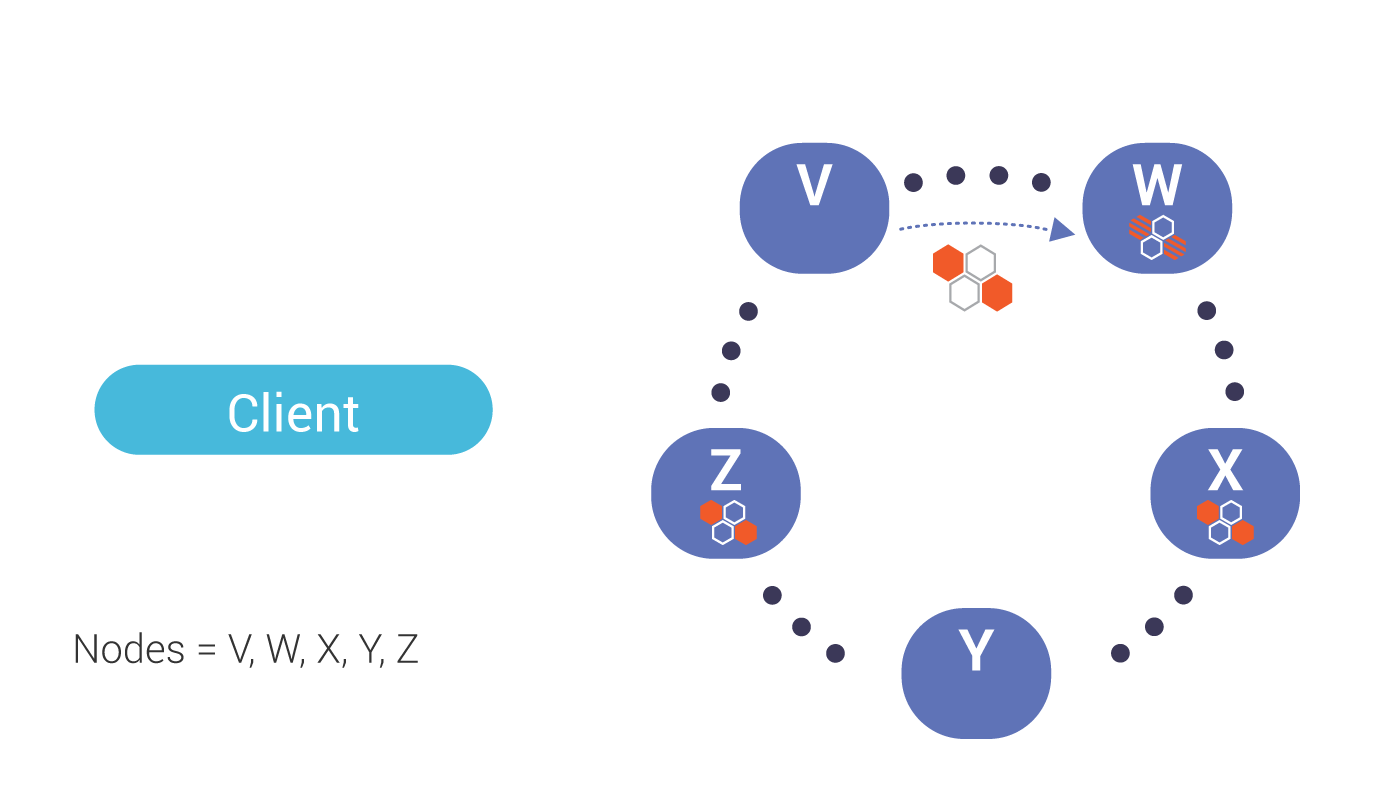
This image illustrates the flow of a read request, when data is out of sync, and a background read repair process is triggered.
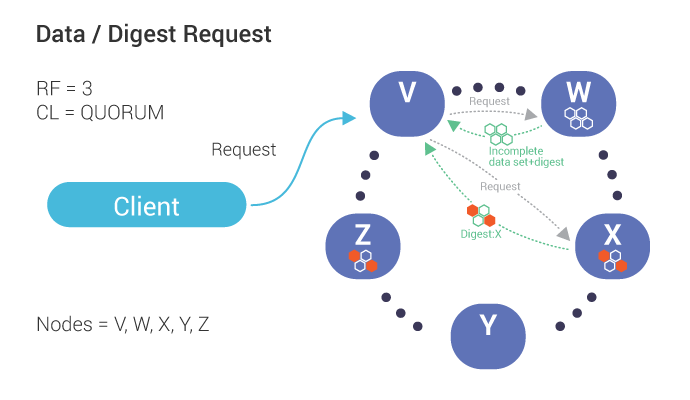
Our coordinator, V, requests data (including digest) from one node, W, which is out of date.
The coordinator also requests digests from the number of nodes up to the consistency level (in this case, Quorum or 2) which, in this case, includes Node X.
If the digests from all replicas match, the coordinator responds to the client with the read data. If there is a mismatch (shown above), a read repair is performed.
Read Repair¶
See the appendices below for the detailed flow.
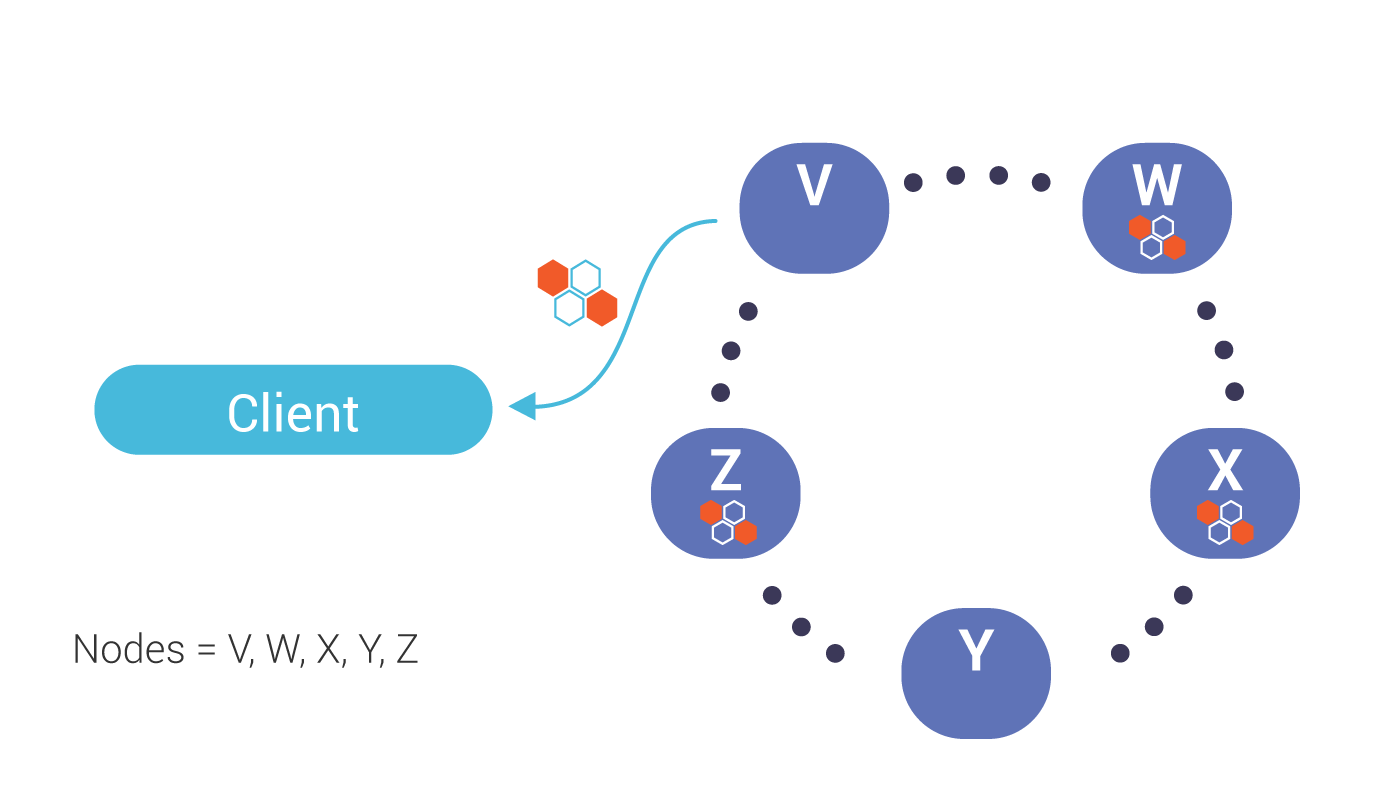
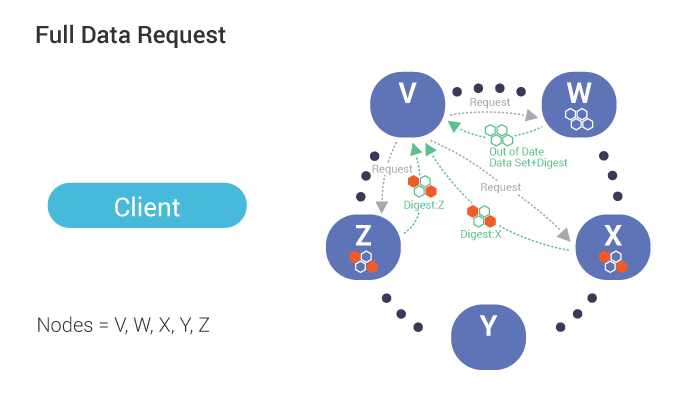
Triggered by a mismatch in digest response from replicas (see above), the co-ordinator, in this case, node V, sends requests (for the full data set) to the same sub set of replicas participates in the read (up to the consistency level).
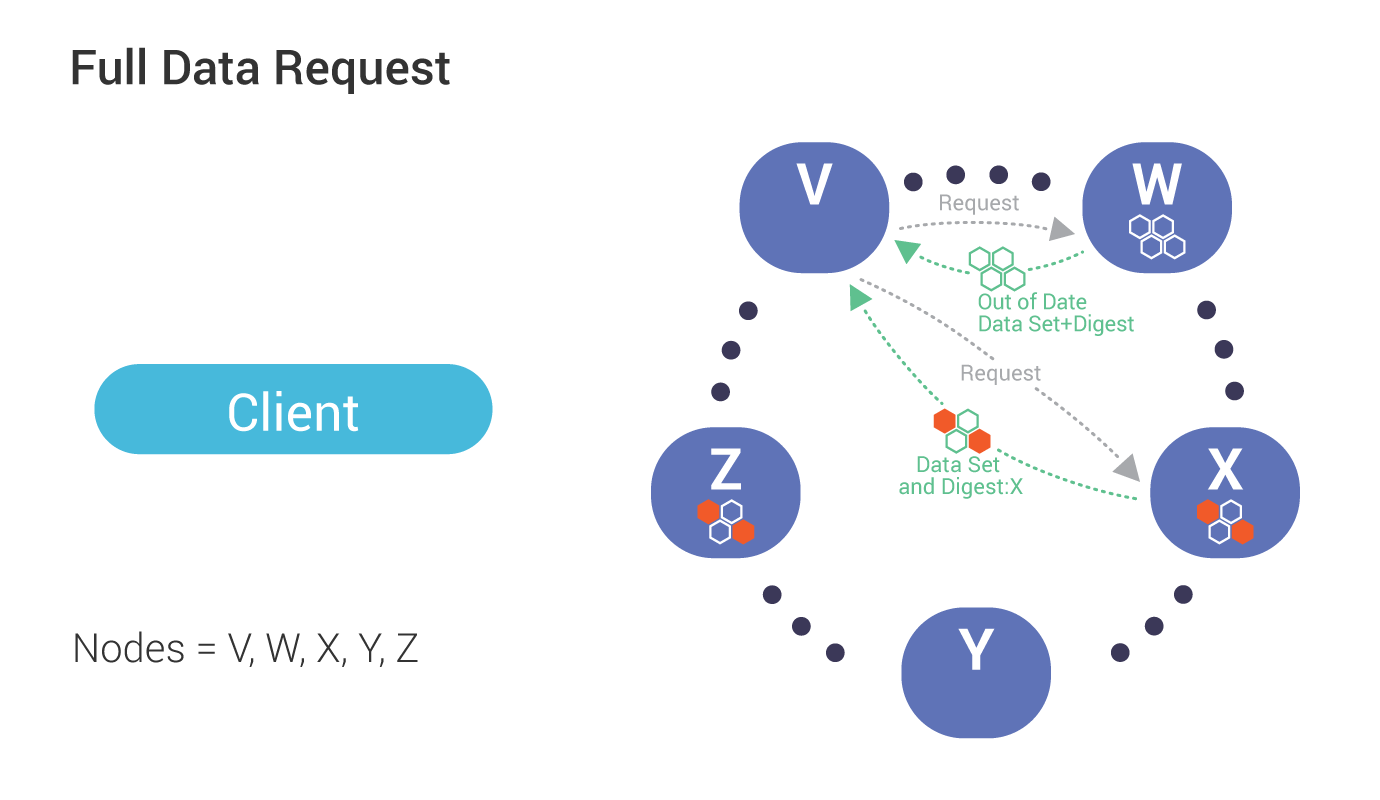
During reconciliation, the co-ordinator (Node V) compares full data sets, and sends updates back to the out-of-date nodes.
Once all updated replicas successfully have responded, the co-ordinator returns the merged data set to the client.
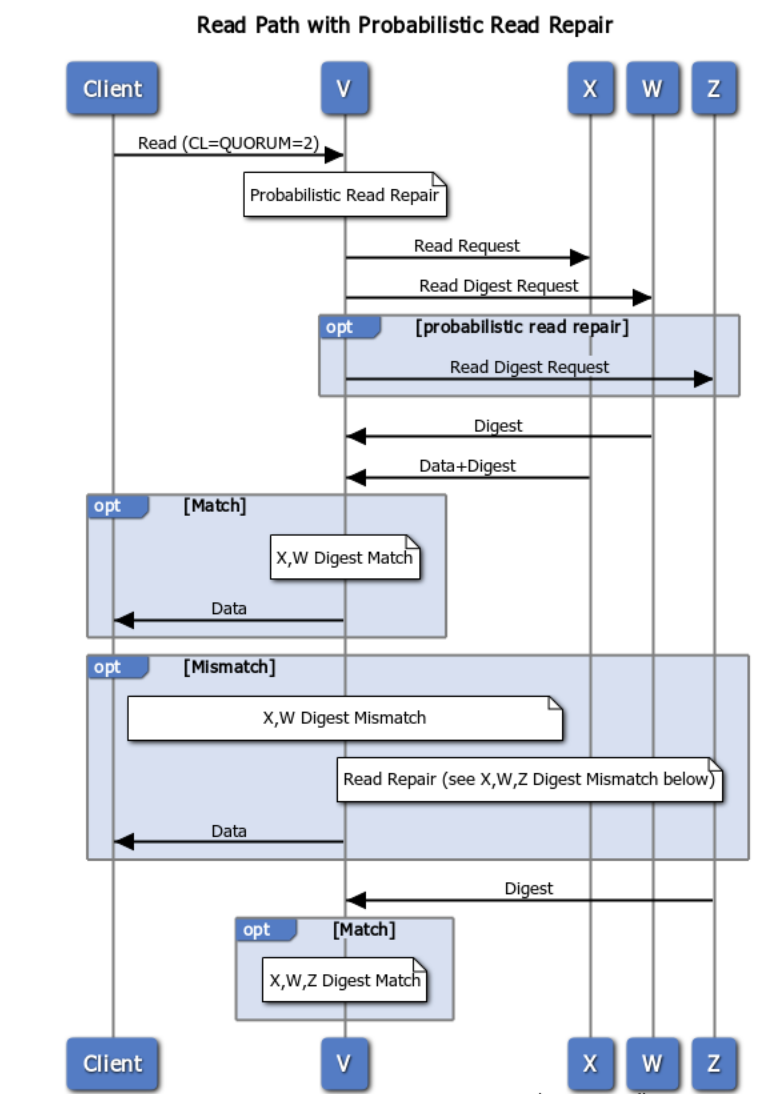
Probabilistic Read Repair¶
See the appendices below for the detailed flow.
Another read repair mechanism is probabilistic read repair, which works as follows:
The coordinator checks the value of the
read_repair_chanceordclocal_read_repair_chance. If the probability of a read repair is triggered, it will start the read repair across the entire cluster, or inside the DC, respectively.
Note
These two settings are configured in scylla.yaml.
In recent Scylla versions (starting from 4.2.0) default value of both parameters is zero, making Probabilistic Read Repair off by default, with a plan to remove it in the future
If the probability of a read repair is triggered, the coordinator sends data request to one of the nodes, digest request to all of the remaining nodes.
The coordinator responds to the client as soon as there are enough replies to achieve consistency level, and there is a match.
After ALL replicas responses to the coordinator (which may have already responded to the client), the coordinator will compare all responses; and if required (there is a mismatch), the coordinator will ask for the data from all replicas, run reconciliation, and send deltas to any out-of-date replica node(s) - in the background.
If a query’s consistency level is more than 1, and a data mismatch is found before consistency level is reached, then the read repair will run in the foreground. All replica nodes are updated before the data is returned to the client. However, if data mismatch is found after a query’s consistency level is achieved, the update happens in the background, as mentioned above.
The probability of this kind of read repair occurring on a read request is based on the read_repair_chance. This setting, provided when a table is created, can apply across data centers. The setting specifies the probability that extra nodes (in addition to those required by the consistency level) are queried for the purpose of read repairs.
A similar setting, dclocal_read_repair_chance, applies only to nodes within the local data center. You can use this setting when conserving traffic between data centers is important.
Appendix¶
Flows created with websequencediagrams.com.